
Even retail investors can invest in hedge funds. One of the low-risk hedge funds is a fund that uses a relative value strategy.
In the relative value strategy, the fund invests based on whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued compared to its intrinsic value. In addition to buying, relative value strategies involve short selling.
However, if you do not invest in hedge funds correctly, you will lose money. In the past, a huge hedge fund that used the relative value strategy went bankrupt. On the other hand, there are hedge funds that have excellent performance.
So I will explain the types of relative value strategies and how to invest in the right hedge funds.
Table of Contents
There Are Several Relative Value Strategies for Hedge Funds
Each hedge fund has a different investment strategy. One of them is the relative value strategy, which is a low-risk investment approach.
In relative value strategies, hedge funds invest in stocks, bonds, forex (currencies), commodity futures, interest rates, and cryptocurrencies. In other words, there are so many investment options. In relative value strategies, when a stock is overvalued, they sell it short. On the other hand, if the stock is undervalued, they buy it.
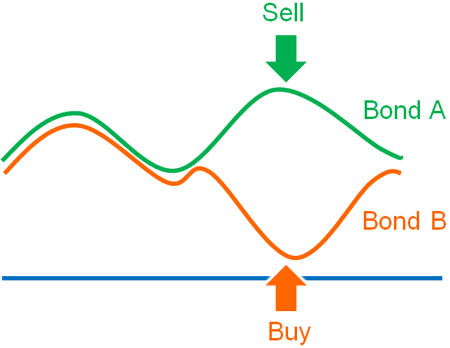
After that, if the price returns to its original level, hedge funds can earn a profit. The investment criterion is whether it is overvalued or undervalued compared to its intrinsic value.
However, among the relative value strategies, there are several methods. Typical relative value strategies are as follows.
- Equity Market Neutral Strategy
- Bond Arbitrage Strategy
- Convertible Bond Arbitrage Strategy
Let’s review the details of each.
Equity Market Neutral Strategy Is Not Dependent on Recession
The market neutral strategy is known as a low-risk investment method. In a market neutral strategy, the fund buys and sells for the same amount of shares.
In the case of a typical hedge fund, the amount of buying and selling is different. There are many hedge funds that make large profits by shorting large amounts of shares. On the other hand, in a market neutral strategy, they buy and sell the same amount, so there is little price movement even if the stock price goes up or down.
Of course, they do not buy and sell the same stock. They judge whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued, and then take a long position (buying) and a short position (selling) in different individual stocks or ETFs (exchange-traded funds).
For example, when stock prices rise, undervalued stocks will rise significantly. On the other hand, the price movement of overvalued stocks is small. Therefore, we can make money from the difference.
Also, when stock prices go down, the price of overvalued stocks goes down significantly. On the other hand, the price movement of undervalued stocks is small. Therefore, we will make money as well.

The equity market neutral strategy allows us to profit whether the market price goes up or down. Therefore, it is not affected by recessions and provides profits with low risk.
Bond Arbitrage Strategy Is Theoretically 100% Profitable
On the other hand, bond arbitrage strategies are also widely used. In the case of stocks, prices frequently do not return to their original levels after prices fall. In the case of bonds, on the other hand, the value of corporate and government bonds rarely continues to decline unless they default.
If you invest in bonds, you can earn dividends. Therefore, the value of bonds rarely drops to zero, and the price of bonds stays almost the same. Even if the value of a bond declines temporarily due to a major recession, the price usually returns to its original value after a few months.
For example, here is the price history of HYG, a bond known for its dividend yield of about 5% per year, compared to the S&P 500, the stock price of the top 500 US companies
- iShares iBoxx $ High Yield Corporate Bond ETF (HYG)
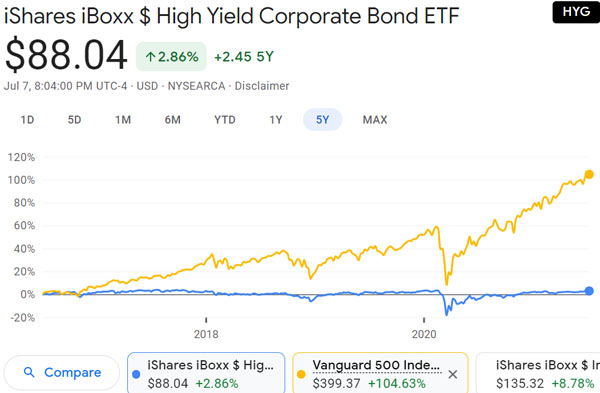
As you can see, the price fluctuation of bonds (HYG) in the blue line is much smaller than that of stocks (S&P 500) in the yellow line. In addition, as mentioned earlier, even if the bond prices fall temporarily, they tend to return to their original level after a few months.
Therefore, the bond arbitrage strategy involves shorting overvalued bonds and buying undervalued bonds.
Unlike the market neutral strategy, a fund does not buy and sell the same amount of bonds. Therefore, although it is different from the market neutral strategy, it is the same in that the fund invests based on whether the investment is overvalued or undervalued. In addition, when bond prices are overvalued or undervalued, they have a tendency to return to their original price, making it a theoretically 100% profitable investment method.
Using a Convertible Bond Arbitrage Strategy
Relative value strategies using convertible bonds are also widely used. Convertible bonds are bonds that have the right to be converted into stocks. Although it is a corporate bond, you should understand that it is a financial instrument with similar characteristics to stocks.
There are many listed companies that issue bonds. Some of them are undervalued convertible bonds compared to the stock price.
So we buy convertible bonds that are undervalued. At the same time, we short the same company’s stock. If the value of the stock goes up, the undervalued convertible bond will have a higher price growth rate. In the case of a decline in value, the price of the undervalued convertible bond is less likely to fall, while the price of the stock is more likely to fall sharply.
Therefore, just like the equity market neutral strategy, we can make profits even if the value of the investment goes up or down.
Many Bankruptcy Cases Even for Low-Risk Investments
These investment strategies are relative value strategies. Although the investment targets are different, such as stocks and bonds, hedge funds invest based on whether the investment is overvalued or undervalued.
The relative value strategy is a low-risk strategy that rarely results in losses. In fact, the bond arbitrage strategy has a theoretically 100% probability of making money. In reality, however, there are many cases of bankruptcy of hedge funds that used the relative value strategy.
One of the most famous is the collapse of LTCM, which was the world’s largest hedge fund at the time, managing over 100 billion US dollars in assets. Also, their investment method was bond arbitrage strategy, which is a low-risk investment method.
However, they lost most of their assets in the Asian financial crisis in 1997 and the Russian financial crisis in 1998 and went bankrupt.
Even if we theoretically have a 100% chance of making money, the financial markets do not work as the theory says. Also, exceptions occur frequently in the financial markets, as evidenced by the fact that a major recession hits every few years. Therefore, even hedge funds that adopt a low-risk investment strategy are not necessarily safe.
An Example of Relative Value Strategy and Yields
If you want to invest in a hedge fund that uses the relative value strategy, be sure to check the hedge fund’s fact sheet. Particularly important is to check what kind of yields they have produced in the past major recessions.
For example, below is a fact sheet for a hedge fund that uses an equity market neutral strategy.
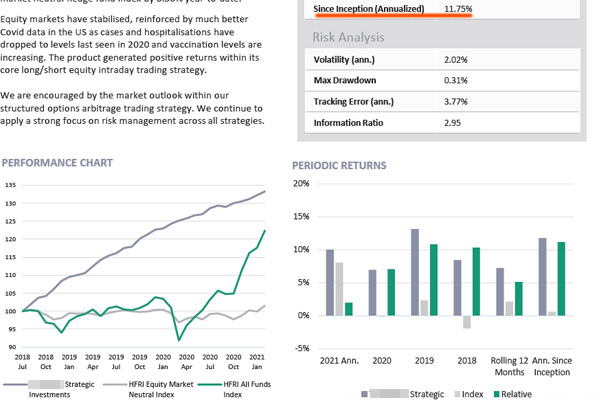
In the case of this hedge fund, the average annual interest rate is 11.75%. It also has small annual volatility of 2.02%. Importantly, the returns were positive in February and March of 2020 when the Corona shock occurred.
If you invest in this hedge fund, you will not be able to earn many times the return during a boom. On the other hand, even in a recession, you will be able to earn a steady 11% annual return.
Be Careful of High Yield Relative Value Strategies
The reason why it is important to check the fact sheet when investing in low-risk hedge funds is that you can distinguish if it is the right hedge fund to invest in.
For example, LTCM, which went bankrupt, had an excellent investment performance in its first four years. The average annual interest rate was 40%, and it was generating great returns. However, the financial crisis caused it to lose most of its assets within a year, and it went bankrupt.
As mentioned above, all relative value strategies are low-risk investment methods. However, despite being a low-risk investment, LTCM had a high yield with an average annual interest rate of 40%. The reason for this is that it traded bonds with high leverage, up to 25 times.
Bond prices fluctuate little. Therefore, they were able to achieve high yields through highly leveraged trading. However, if we invest with high leverage, one big mistake can cause us to lose most of our assets and go bankrupt.

Therefore, don’t invest in hedge funds that use a relative value strategy with a high yield. In this case, there is a high possibility that they are trading with high leverage. As a result, there is a high risk that the fund will fail during a financial crisis like LTCM.
Also, check the fact sheets to see what kind of investment performance they had during the past financial crisis. Then you can decide if it is a hedge fund you should invest in or not.
Get a Stable Yield with Relative Value Strategy
A low-risk investment strategy for hedge funds is the relative value strategy. Hedge funds invest in stocks, bonds, currencies, and commodity futures based on whether the prices are overvalued or undervalued. One of the characteristics of the relative value strategy is to buy and sell short at the same time.
There are also multiple methods of relative value strategies, such as the equity market neutral strategy and the bond arbitrage strategy. All of these strategies are low-risk investment methods.
However, in the past, there have been a number of hedge funds that have used the relative value strategy and have gone bankrupt. So be careful of hedge funds with high-yielding relative value strategies. Also, check the fact sheet to see the past investment performance.
Hedge funds that use a relative value strategy can increase your assets with low risk. However, there are some hedge funds that are not good, so it is a good idea to check what their past investment performance has been to avoid failure.









